Many of the B2B connections are still making use of an AS2-connection to exchange documents. Below you will be able to find out how this can be configured in BizTalk Server and Azure Integration Services.
But before we can dive into the how, let’s start with the what; what is the AS2-protocol and how does it work.
Steps
- What is AS2
- Getting Started
- How to configure Microsoft BizTalk Server
- How to configure Azure Integration Services
- Conclusion
What is AS2
AS2, or Applicability Statement 2, is an HTTP-based protocol used to transmit messages in a fast and secure manner, primarily used for the business-to-business exchange of documents.
But how does it work?
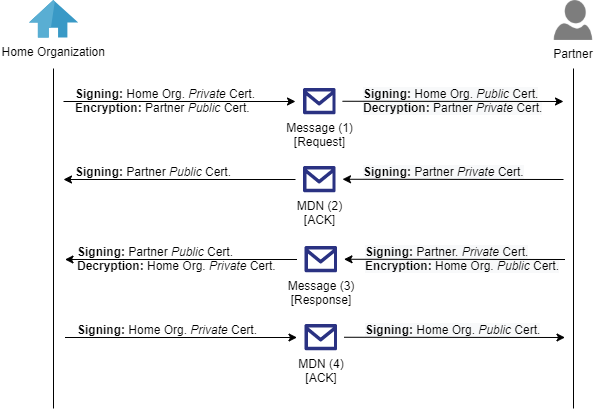
Each message that is to be transmitted towards a specific receiver, can be encrypted and/or can be signed. Can because even though most of the time both are being enabled, this is not a strict requirement for making use of this protocol.
Next to this, each message should be replied by a sync or async MDN (or Message Disposition Notification), which is a technical acknowledgment that indicates the message has been successfully received, has been decrypted and of which the signature has been verified.
In the diagram below, you can see a graphical representation of the exchange of these messages.
Getting Started
Before you can start configuring the AS2-connection, there are a couple of prerequisites you will need:
- Home Organization Certificate
- Home Organization connection details
- Partner Certificate
- Partner connection details
Home Organization Certificate
As you can see in the above overview, it is the private certificate of the home organization that is used to sign the outgoing messages or to decrypt the incoming messages.
Therefore it is important that before starting with any configuration you obtain this certificate.
IMPORTANT:
Store this private certificate in a secure location and make sure you never share the password of this certificate with anyone outside of your organization. If you do share this password, that means other people can impersonate themselves as being part of your organization and exchange falsified documents on your behalf.
A certificate can be obtained by buying it from one of the certified authorities (eg. DigiCert, GoDaddy, …) OR you could generate a self-signed certificate by using the below command which generates one and stores it within your user-specific personal certificate store:
makecert -r -pe -n "CN=Home organization AS2 SHA256" -b 03/31/2022 -e 04/01/2024 -eku 1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.1 -ss my "HomeOrganization.AS2.SHA256.cer" -sr currentuser -sky exchange -sp "Microsoft RSA SChannel Cryptographic Provider" -sy 12 -a "sha256" -nscp -len 2048
NOTE: Whether you are buying or generating a certificate, from a security perspective, it is advised to use environment-specific certificates.
One of the requirements for the certificate you want to use for AS2-communication is that the Key Usage attribute of a certificate must match the certificate’s use:
- Certificates used for AS2 transport must have the attributes required for their intended use.
- For signing and signature verification, the Key Usage attribute of the certificate must be Digital Signature.
- For encryption and decryption, the Key Usage attribute of the certificate must be Data Encipherment or Key Encipherment.
You can verify the Key Usage attribute by double-clicking the certificate, clicking the Details tab in the Certificate dialog box, and checking the Key Usage field. For more information on these requirements, have a look overe here
Home Organization connection details
Setting up an AS2-connection requires quite some toggles to be switched, which should be matched by the configuration that is to be set up in the system of your partner.
So it’s best to make sure you always have at least the following details at hand:
- AS2 endpoint:
What is the publicly accessible endpoint which can be used by partners to deliver documents - Public IP:
List your public IP address which will be used to sent documents from to your partner, as they might have a firewall in place limiting access to their endpoint. - AS2 Identifier:
How will your system identify itself against the outside world? This value will be used to identify which configuration settings should be used during the decryption or validation process.
Try and stick to the same value as your and your partners’ configuration will depend on it. - Hashing algorithm:
The algorithm used by this party when signing the message, for example: SHA1. - Encryption algorithm:
The algorithm used by this party when encrypting the message, for example: DES3. - MDN Settings:
- Is an MDN required?
This is advised, as it is a technical acknowledgment by the receiver’s system, specifying the document has been received successfully.
Note: This is a confirmation that the document has been received, NOT that it has been processed, which is important to understand. - Does the MDN have to be signed and if so, what algorithm is used?
Indicates whether to send the MDN as plain text or signed, using the same certificate as the main payload. - Sync vs Async?
Should the MDN be returned as a direct response to the transmission of the main payload, or should it be sent as a separate message, to an AS2-endpoint?
- Is an MDN required?
Partner Certificate
To configure the connection to use the appropriate certificate for encrypting the outbound document or verify the signing of the incoming document, you need to obtain a copy of the public certificate from your partner.
As opposed to the home organization certificate this is not something you can help out with. This certificate should be bought/generated by the partner organizations themselves.
Partner connection details
Again some more connection details should be known before you can configure the AS2 connection, but this time the details should come from your partners’ system:
- AS2 endpoint:
The publicly accessible endpoint where documents should be sent towards. - Public IP:
If you have a firewall in place, you should request the public IP address of their system, for you to configure a new firewall rule to accept the traffic. - AS2 Identifier:
As mentioned earlier, this is the unique identifier that will be used during the validation process to identify the settings to use. - Hashing algorithm: See above
- Encryption algorithm: See above
- MDN Settings: See above
How to configure Microsoft BizTalk Server
Requirements:
- Microsoft BizTalk Server with EDI and AS2 Status reporting feature
The table below will indicate the locations where you need to import the different certificates. When you have configured everything, but the connection is still failing, make sure to double-check whether the imported certificates are in the correct location, as mentioned in the table.
| Message or MDN | Direction | Certificate Type | Certificate Owner | Public Or Private | Certificate Location | Where to configure in BizTalk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Message (1) | Outbound | Signing | Home Org. | Private | Personal certificate store of in-proc host user | BizTalk Group / Properties / Certificate |
| Message (1) | Outbound | Encryption | Partner | Public | Other People certificate store of local computer | Send Port / Certificate |
| MDN (2) | Inbound | Signing | Partner | Public | Other People certificate store of local computer | Party / Certificate |
| Message (3) | Inbound | Signing | Partner | Public | Other People certificate store of local computer | Party / Certificate |
| Message (3) | Inbound | Decryption | Home Org. | Private | Personal certificate store of in-proc host user | Isolated Host / Certificates (Seems to be optional) |
| MDN (4) | Outbound | Signing | Home Org | Private | Sync MDN: Personal certificate store of isolated host user | BizTalk Group / Properties / Certificate |
| Async MDN: Personal certificate store of in-proc host user |
Note: you can combine this table with the schema shared earlier to visualize which certificate is used in which step.
How to configure Azure Integration Services
Requirements:
- Azure Integration Account
- Azure Logic App
As before, the below table will give you an overview of which certificate is used in which step and where these certificates need to be imported and/or configured.
| Message or MDN | Direction | Certificate Type | Certificate Owner | Public Or Private | Certificate Location | Where to configure in AIS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Message (1) | Outbound | Signing | Home Org. | Private | Import the private certificate into Azure Key Vault and link it with the public certificate in the Integration Account | Integration Account / Agreement / Send Settings / Signing certificate |
| Message (1) | Outbound | Encryption | Partner | Public | Add the certificate in the Integration Account | Integration Account / Agreement / Send Settings / Encryption certificate |
| MDN (2) | Inbound | Signing | Partner | Public | Add the certificate in the Integration Account | Integration Account / Agreement / Receive Settings / Signing certificate |
| Message (3) | Inbound | Signing | Partner | Public | Add the certificate in the Integration Account | Integration Account / Agreement / Receive Settings / Signing certificate |
| Message (3) | Inbound | Decryption | Home Org. | Private | Import the private certificate into Azure Key Vault and link it with the public certificate in the Integration Account | Integration Account / Agreement / Receive Settings / Encryption certificate |
| MDN (4) | Outbound | Signing | Home Org | Private | Import the private certificate into Azure Key Vault and link it with the public certificate in the Integration Account | Integration Account / Agreement / Send Settings / Signing certificate |
Home Organization setup
Upload the private certificate into Azure Key Vault
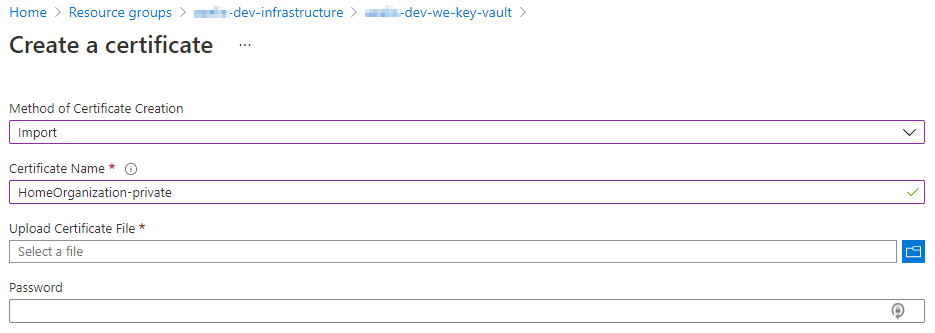
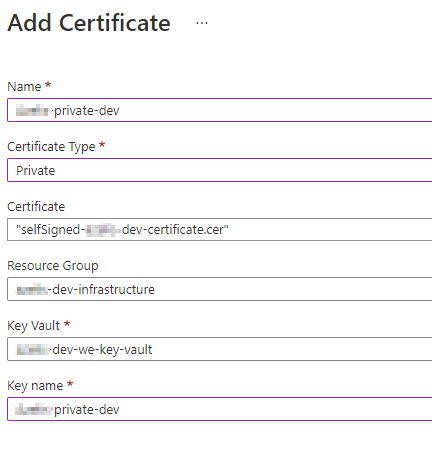
Create a new Private certificate in the Integration Account.
While creating the new Private certificate, you will be asked to upload the public certificate under the “Certificate”-property, while the private part of the certificate will be referenced directly from the Azure Key Vault.
Be sure to grant the “Azure Logic Apps” service principal (7cd684f4-8a78-49b0-91ec-6a35d38739ba) access to Key Vault by creating an access policy with at least the following certificate-permissions: list, get, decrypt, sign key-permissions, get/list.
Create a new “Partner” in the Integration Account and make sure to add the AS2Identity-qualifier.

Partner setup
Create a new “Public” certificate in the Integration Account.
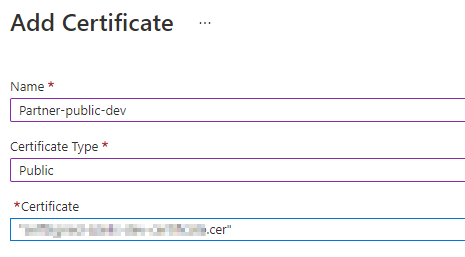
Create a new “Partner” in the Integration Account and make sure to add the AS2Identity-qualifier.
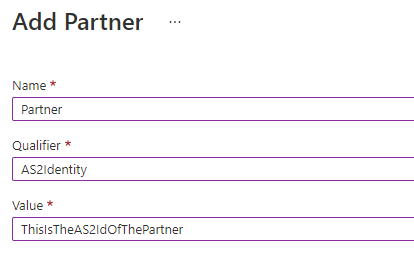
Create an AS2-agreement
In the Integration Account, create a new agreement linking the Home Organization with the Partner and make sure to configure all receive/send settings as agreed upon between the 2 parties.
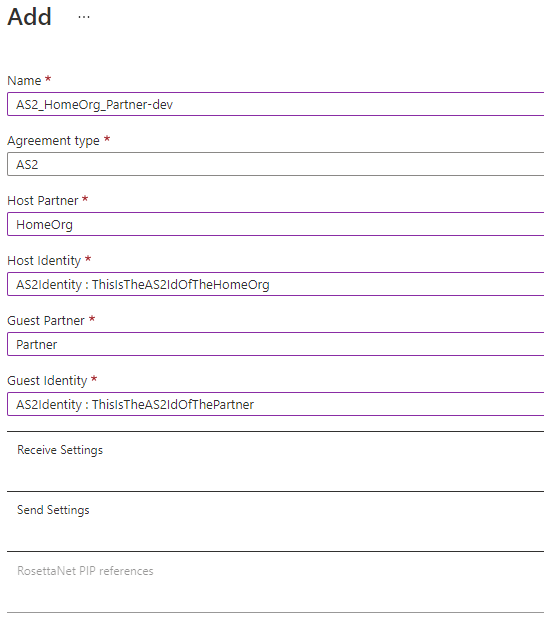
Conclusion
While setting up an AS2-connection might seem complex at first, as soon as you’ve got it up and running once, it shouldn’t scare you off anymore. But, if it would, you can always refer back to 1 of the tables listed above.